티스토리 뷰
1.1-1. Of a group of patients having injuries, 28% visit both a physical therapist and a chiropractor and 8% visit
neither. Say that the probability of visiting a physical therapist exceeds the probability of visiting a chiropractor
by 16%. What is the probability of a randomly selected person from this group visiting a physical therapist?
1.1-1. 부상을 입은 환자들 중 28%가 물리치료사와 카이로프랙터를 모두 방문하고 8%는 어느 쪽도 방문하지 않았습니다. 물리치료사를 방문할 확률이 카이로프랙터를 방문할 확률보다 16% 높다고 합시다. 이 그룹에서 임의로 선택된 사람이 물리치료사를 방문할 확률은 얼마인가요?

P(A): 물리치료사를 방문할 확률
P(B): 카이로프렉터를 방문할 확률
물리치료사를 방문할 확률이 카이로프랙터를 방문할 확률보다 16% 높다고 합시다
-> P(A) = P(B) +0.16
P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
0.92 = 2P(A) - 0.16 - 0.28
=0.68
1.1-2. An insurance company looks at its auto insurance customers and finds that (a) all insure at least one car, (b)
85% insure more than one car, (c) 23% insure a sports car, and (d) 17% insure more than one car, including a
sports car. Find the probability that a customer selected at random insures exactly one car and it is not a sports car.
1.1-2. 어떤 보험 회사는 자동차 보험 고객들을 살펴보고 (a) 모두 최소한 한 대의 차를 보험 가입하고 있으며, (b) 85%가 두 대 이상의 차를 보험 가입하고 있으며, (c) 23%가 스포츠 카를 보험 가입하고 있으며, (d) 17%가 두 대 이상의 차와 함께 스포츠 카를 보험 가입하고 있다고 합니다. 임의로 선택된 고객이 정확히 한 대의 차를 보험 가입하고 있으며 그 차가 스포츠 카가 아닌 확률은 얼마인가요?

두개 이상의 차를 가질 확률
P(A) = 0.85
스포츠 카를 가질 확률
P(B) =0.23
두 개이상의 차와 스포츠카를 가질 확률
P(A ∩ B) =0.28
두 개 이상의 차 혹은 스포츠카를 가질 확률
P(AUB) = 0.85 + 0.23 - 0.28 =0.91
한 개의 차와 스포츠카를 가지지 않을 확률
1- P(A U B) = 0.09
1.1-3. Draw one card at random from a standard deck of cards. The sample space S is the collection of the 52 cards.
Assume that the probability set function assigns 1/52 to each of the 52 outcomes. Let
A = {x: x is a jack, queen, or king},
B = {x: x is a 9, 10, or jack and x is red},
C = {x: x is a club},
D = {x: x is a diamond, a heart, or a spade}.
Find (a) P(A), (b) P(A ∩ B), (c) P(A ∪ B), (d) P(C ∪ D), and (e) P(C ∩ D).
1.1-3. 표준 카드 덱에서 임의로 한 장의 카드를 뽑을 경우, 표본 공간 S는 52장의 카드로 이루어져 있습니다. 확률집합 함수는 각각의 52개의 결과에 1/52의 확률을 할당한다고 가정합니다. 이때, A, B, C, D를 다음과 같이 정의하겠습니다:
Find (a) P(A), (b) P(A ∩ B), (c) P(A ∪ B), (d) P(C ∪ D), and (e) P(C ∩ D).
(a)
\( P(A) = \frac{3 \times 4}{13 \times 4}= \frac{12}{52}\)
각각의 카드는 13개씩 4개의 종류가 있고 그 중에 3개(잭,퀸 킹)이 4가지 종류가 있다.
(b)
\(P(B) = \frac{3 \times 2 }{52}\)
\(P ( A \cap B) = \frac{2 \times 1}{52}\)
잭은 13개 카드 중에 하나씩 있고, 빨강은 2종류가 있다.
(c)
\(P(A \cup B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \cap B) = \frac{12}{52} + \frac{6}{52} - \frac{2}{52} = \frac{16}{52}\)
(d)
\(P(C) = \frac{13}{52}=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(P(D) = \frac{13 \times 3}{52} = \frac{3}{4}\)
C와 D는 배반사건이기 때문에 교집합이 없다.
d=1
{e}
P(C ∩ D)=0이 된다.
1.1-4. A fair coin is tossed four times, and the sequence of heads and tails is observed.
(a) List each of the 16 sequences in the sample space S.
(b) Let events A, B, C, and D be given by A = {at least 3 heads}, B = {at most 2 heads}, C = {heads on the third toss}, and D = {1 head and 3 tails}. If the
probability set function assigns 1/16 to each outcome in the sample space,
find (i) P(A), (ii) P(A ∩ B), (iii)P(B), (iv) P(A∩C), (v) P(D), (vi) P(A∪C), and (vii) P(B ∩ D).
1.1-4. 공정한 동전이 네 번 던져지고, 앞면과 뒷면의 시퀀스가 관찰됩니다.
(a) 표본 공간 S의 16개 시퀀스를 나열합니다.
(b) 사건 A, B, C, D를 다음과 같이 정의하며, 각 결과에 대한 확률 집합 함수가 1/16로 할당된다고 가정합니다:
find (i) P(A), (ii) P(A ∩ B), (iii)P(B), (iv) P(A∩C), (v) P(D), (vi) P(A∪C), and (vii) P(B ∩ D).
(i)
P(A) = 4!/3! +1= 5
-> 앞면이 3번, 앞면이 4번 -> 5/16
(ii)
P(B) = 앞면이 0, 앞면이 1, 앞면이 2
1 + 4!/3! + 4!/2!2! = 1 + 4 +6 = 11 -> 11/16
P(A ∩ B) = 0 (하나는 최대 두번, 하나는 최소 3번)
(iii)
P(B) = 앞면이 0, 앞면이 1, 앞면이 2
1 + 4!/3! + 4!/2!2! = 1 + 4 +6 = 11 -> 11/16
(iv)
P(A ∩ C) = 앞면이 세번째에 나오고, 앞면이 3개인 경우
{앞, 앞, 뒤} 3!/2! =3 + {앞, 앞, 앞} = 1 =4
4/16
{v}
4!/3! = 4/16
{vi} = P(A) + P(C) - P(A ∩ C) = 5/16 + 8/16 - 4/16 = 9/16
P(C) = 2x2x2= 8
{vii}
P (B ∩ D) = 앞면이 한번 나올 확률 = 4/16
1.1-5. Consider the trial on which a 3 is first observed in successive rolls of a six-sided die. Let A be the event that
3 is observed on the first trial. Let B be the event that at least two trials are required to observe a 3. Assuming that
each side has probability 1/6, find (a) P(A), (b) P(B), and (c) P(A ∪ B).
1.1-5. 여섯 면 주사위를 연속으로 굴렸을 때, 처음으로 3이 나오는 시도를 고려해 봅시다. A를 첫 번째 시도에서 3이 나오는 사건이라고 정의하고, B를 최소 두 번 시도가 필요한 경우에 3이 나오는 사건이라고 정의합니다. 각 면이 나올 확률이 1/6이라고 가정할 때, (a) P(A), (b) P(B), 그리고 (c) P(A ∪ B)를 찾아봅시다.
P(A) = 1/6
P(B) = 처음에 3이 나오면 안되니까 나머지 5개의 눈이 나올 확률 5/6
P(A U B) =1 (둘은 배반 사건)
1.1-6. If P(A) = 0.4, P(B) = 0.5, and P(A∩B) = 0.3,
find (a) P(A ∪ B), (b) P(A ∩ B'), and (c) P(A' ∪ B').
(a)
P(AUB) =P(A) +P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
=0.4+0.5-0.3 = 0.6
(b)
P( A ∩ B') = P(A - B) = P(A) - P(A ∩ B) = 0.4-0.3=0.1
(c)
P(A' U B')= P(( A ∩ B)') = 1-0.3=0.7
1.1-7. Given that P(A ∪ B) = 0.76 and P(A ∪ B') = 0.87,
find P(A).

초록색 부분이 0.87, 노란색 부분은 0.13
A U B - 노란색 부분 = P(A)
0.76 - 0.13 = 0.63
1.1-8. During a visit to a primary care physician’s office, the probability of having neither lab work nor referral to a
specialist is 0.21. Of those coming to that office, the probability of having lab work is 0.41 and the probability of
having a referral is 0.53.What is the probability of having both lab work and a referral?
1.1-8. 제일 의사의 진료실을 방문할 때, 실험에서 검사나 전문의로의 추천을 받지 않을 확률은 0.21입니다. 그 진료실을 찾는 사람들 중에서 검사를 받을 확률은 0.41이며, 전문의로부터 추천을 받을 확률은 0.53입니다. 검사를 받고 전문의로부터 추천을 받을 확률은 얼마인가요?

P(A) + P(B) - P( A ∩ B) = P(A U B)0.41 + 0.53 - P (A ∩ B) = 0.79P(A ∩ B) = 0.15
1.1-9. Roll a fair six-sided die three times. Let A1 ={1 or 2 on the first roll}, A2 = {3 or 4 on the second roll},
and A3 = {5 or 6 on the third roll}. It is given that P(Ai) = 1/3, i = 1, 2, 3; P(Ai ∩ Aj) = (1/3)^2, i != j; and
P(A1 ∩ A2 ∩ A3) = (1/3)^3.
(a) Use Theorem 1.1-6 to find P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪ A3).
(b) Show that P(A1 ∪ A2 ∪ A3) = 1 − (1 − 1/3)^3.

\( P(A \cup B \cup C) = P(A) + P(B) +P(C) - P(A \cap B) - P(A \cap C) P(B \cap C) +P(A \cap B \cap C)\)이다
위의 문제에 따라
\(P(A_1)= P(A_2) = P(A_3) = \frac{1}{3}, P(A_1 \cap A_2) = P(A_2 \cap A_3) = P(A_1 \cap A_3) = (\frac{1}{3})^2, P(A_1 \cap A_2 \cap A_3) = (\frac{1}{3})^3\)이므로 답은 3*(1/3) -3(1/3)^2 +(1/3)^3
1.1-10. Prove Theorem 1.1-6.
1.1-11. A typical roulette wheel used in a casino has 38 slots that are numbered 1, 2, 3, . . . , 36, 0, 00, respectively.
The 0 and 00 slots are colored green. Half of the remaining slots are red and half are black. Also, half of the
integers between 1 and 36 inclusive are odd, half are even, and 0 and 00 are defined to be neither odd nor even. A
ball is rolled around the wheel and ends up in one of the slots; we assume that each slot has equal probability of
1/38, and we are interested in the number of the slot into which the ball falls.
(a) Define the sample space S.
(b) Let A = {0, 00}. Give the value of P(A).
(c) Let B = {14, 15, 17, 18}. Give the value of P(B).
(d) Let D = {x : x is odd}. Give the value of P(D).
1.1-11. 일반적인 카지노에서 사용되는 룰렛 휠은 1, 2, 3, ..., 36, 0, 00으로 번호가 매겨진 38개의 슬롯이 있습니다. 0과 00 슬롯은 녹색으로 색칠되어 있습니다. 나머지 슬롯의 절반은 빨강이고 나머지 절반은 검정입니다. 또한 1부터 36까지의 정수 중 절반은 홀수이고, 나머지 절반은 짝수입니다. 0과 00은 홀수도 짝수도 아닙니다. 공이 휠 주위를 굴러 돌며 슬롯 중 하나에 떨어지게 됩니다. 각 슬롯이 등장할 확률이 동일하다고 가정하고, 공이 떨어지는 슬롯의 번호에 관심이 있습니다.
(a) 표본 공간 S를 정의하세요.
(b) A = {0, 00}로 정의하세요. P(A)의 값을 제시하세요.
(c) B = {14, 15, 17, 18}로 정의하세요. P(B)의 값을 제시하세요.
(d) D = {x : x가 홀수인 경우}로 정의하세요. P(D)의 값을 제시하세요.
(a)
S={1,2,3, ..., 0,00}
(b)
P(A) = 2/38
(c)
P(B) = 4/38
(d)
P(D)18/38
1.1-12. Let x equal a number that is selected randomly from the closed interval from zero to one, [0, 1]. Use your intuition to assign values to
(a) P({x: 0 ≤ x ≤ 1/3}).
(b) P({x: 1/3 ≤ x ≤ 1}).
(c) P({x: x = 1/3}).
(d) P({x: 1/2 < x < 5}).
1.1-12. x를 0부터 1까지의 닫힌 구간에서 무작위로 선택된 수로 가정합니다. 직관에 따라 에 어떤 값들을 할당할 수 있을까요?
(a)
[0, 0.1, ..., 0.33 ..]
(b)
[0.34, 0.35, ..., 1]
(c)
1/3
(d)
[..., 0.51, ..., 4,5]
1.1-13. Divide a line segment into two parts by selecting a point at random. Use your intuition to assign a probability
to the event that the longer segment is at least two times longer than the shorter segment.
1.1-13. 선분을 임의로 한 점을 선택하여 두 부분으로 나눕니다. 직관에 따라 긴 세그먼트가 짧은 세그먼트보다 최소 두 배 길다는 사건에 확률을 할당해 보세요.
->2/3

직선이 빨간색 범위 안에만 안들어가면 어떤 곳에 선을 그려도 최소 두배 이상이 된다.
안 되는 범위 1/3, 되는 범위는 1- 1/3 =2/3
1.1-14. Let the interval [−r, r] be the base of a semicircle. If a point is selected at random from this interval, assign
a probability to the event that the length of the perpendicular segment from the point to the semicircle is less
than r/2.
1.1-14. [−r, r] 간격을 반원의 기저로 하겠습니다. 만약 이 간격에서 임의의 점을 선택한다면, 그 점에서 반원까지의 수직 세그먼트의 길이가 r/2보다 작은 사건에 확률을 할당해 보세요.

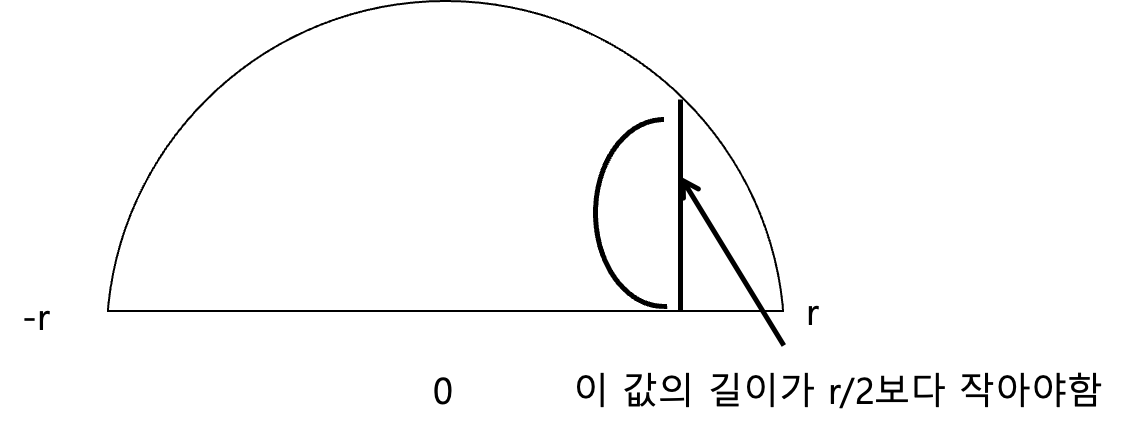

여기서 y값( [-r, r] 사이에서 반원에 수직으로 내린 값)이 \(\frac{1}{2r}\)보다 작아야 한다.
\(y = \sin{\theta } \times r \)이다.
\(\sin{\theta} \times r < \frac{1}{2} \times r\)이므로,
\(\sin{\theta} < \frac{1}{2}\)
\(\theta < 30^{\circ}\)
위에서 구한 30도라는 값을 바탕을 [-r, r]의 수평선 범위로 가져오면,

\(P(A) = \frac{2(r- \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times r)}{2 \times r}\)
1.1-15. Let S = A1 ∪ A2 ∪ . . . ∪ Am, where events A1,A2, . . . ,Am are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
(a) If P(A1) = P(A2) = . . . = P(Am), show that P(Ai) = 1/m, i = 1, 2, . . . ,m.
(b) If A = A1 ∪A2∪. . .∪Ah, where h < m, and (a) holds, prove that P(A) = h/m.
1.1-15. 이벤트 A1, A2, ..., Am이 서로 배타적이고 전체집합을 포괄하는 경우에 S = A1 ∪ A2 ∪ ... ∪ Am으로 정의합니다. (a) 만약 P(A1) = P(A2) = ... = P(Am)이라면, P(Ai) = 1/m (i = 1, 2, ..., m)임을 보여주세요. (b) A = A1 ∪ A2 ∪ ... ∪ Ah인 경우에, 이때 P(A)는 어떤 관계를 가질까요?
1.1-16. Let pn, n = 0, 1, 2, . . . , be the probability that an automobile policyholder will file for n claims in a five-year period. The actuary involved makes the assumption that pn+1 = (1/4)pn. What is the probability that the holder will file two or more claims during this period?
1.1-16. 자동차 보험 가입자가 5년 동안 n회의 청구를 제출할 확률을 pn, n = 0, 1, 2, ..., 로 정의합니다. 관련된 계리사는 가정으로 pn+1 = (1/4)pn을 사용합니다. 이 기반으로 이 기간 동안 보험 가입자가 두 번 이상 청구를 제출할 확률은 무엇일까요?
모든 확률의 합은 1이기에
\(\sum p_n = 1\)
무한등비급수 공식에 의해\(\frac{a}{1-r} ,r= \text{공비}, a=\text{초항}\)
\(\frac{p_0}{1-\frac{1}{4}}= 4 \times p_0 = 3, p_0 = \frac{3}{4}\)
\(p_{n+1} = \frac{1}{4} p_n\)
\(p_{1} = \frac{1}{4} p_0\)
두 번 이상 청구할 확률은 1번 이하 청구할 확률을 전체에서 빼면,
\( 1 - p_{1} -p_0 = 1 - \frac{1}{4} \times \frac{3}{4} - \frac{3}{4} =\frac{1}{16}\)
'통계학 > Hogg 확률과 통계적 추론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 1-4. 독립사상 문제풀이 (0) | 2024.03.15 |
|---|---|
| 1-3 조건부확률 (1) | 2024.02.27 |
| 1-2 연습문제풀이 (1) | 2024.02.25 |
| 1.2 경우의 수 (1) | 2024.02.24 |
| 제1장 확률 (0) | 2024.02.22 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 회계
- stl
- 심리학
- 일본어문법무작정따라하기
- 뇌와행동의기초
- C/C++
- 윤성우
- 보세사
- jlpt
- 오블완
- 코딩테스트
- C
- 티스토리챌린지
- 인지부조화
- K-MOOC
- 일본어
- 류근관
- 여인권
- 사회심리학
- 인프런
- 통계학
- c++
- 일문따
- 백준
- 파이썬
- 정보처리기사
- 열혈프로그래밍
- 데이터분석
- Python
- EBS
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |

